SCAMPER, the creative thinking tool proposed by Alex Faickney Osborn, has long served as a popular method to inspire innovation and improve existing ideas, products, or processes.
However, like any tool, it has its limitations. Definitions of certain thinking techniques within SCAMPER are often unclear, overlapping, and subject to various interpretations. For instance, the boundaries between “Substitute,” “Adapt,” and “Modify” can be ambiguous, while “Put to other uses” is often seen as a variation of “Adapt.” Additionally, the “R” component can be interpreted as either “Reverse” or “Rearrange,” representing two distinct thinking approaches. Furthermore, some essential innovation perspectives are absent from the SCAMPER framework, such as actively considering limitations as a driving force for creativity.
In light of these challenges, I present an enhanced version of the SCAMPER framework. This refined approach introduces seven distinct thinking techniques, providing a more comprehensive and effective framework for fostering innovation.
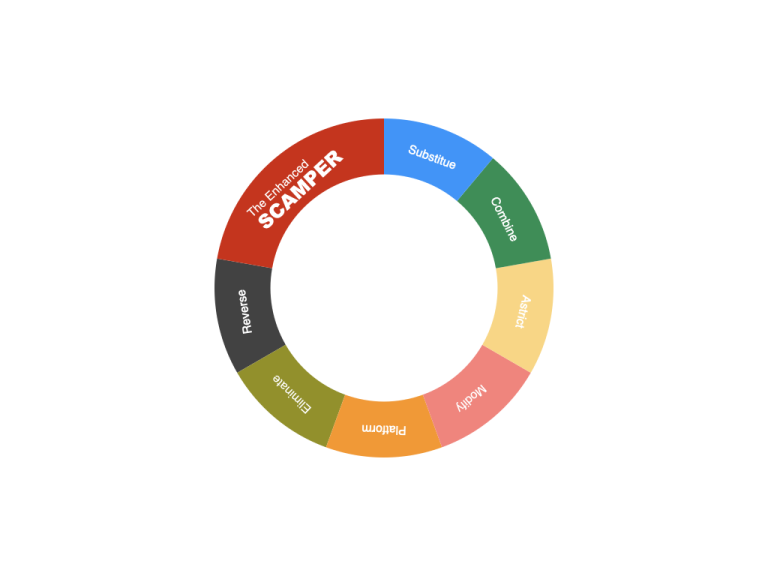
S – Substitute: Explore the possibilities of replacing elements or features with alternative ones. For example, consider substituting materials, functions, or designs within a product.
C – Combine: Generate new ideas by combining different elements or features, particularly at the system, product, and module levels. Think of innovative combinations like integrating payment and mobile technology into a single product.
A – Astrict: Embrace limitations and transform organizational, technological, or product disadvantages into advantages. For instance, explore how Apple’s closed ecosystem brings security benefits.
M – Modify: Focus on modifying or improving existing elements or features, emphasizing the potential for innovation through reconfiguration. Consider rearranging product layouts or sequences to create a fresh user experience.
P – Platform: Collaborate with stakeholders and leverage platforms as avenues for concurrent innovation. Explore opportunities akin to Apple’s App Store.
E – Eliminate: Identify elements or features that can be removed or reduced to simplify products or processes. Focus on streamlining functionalities, interface designs, participant roles, and eliminating unnecessary steps. For example, eliminate redundant features or steps within a product.
R – Reverse: Challenge assumptions and adopt unconventional perspectives by viewing problems or challenges from opposing or unusual angles. Drive innovation by reversing structures, processes, problem statements, viewpoints, and assumptions. Consider adopting different perspectives or exploring the viewpoints of diverse stakeholders to uncover distinct needs and solutions.
By enhancing the SCAMPER framework with these modifications, I consolidate “Adapt,” “Modify,” “Rearrange,” and “Put to other uses” into the comprehensive “Modify” category. Additionally, I introduce two new thinking techniques: “Astrict” and “Platform.” These enhancements refine the innovation process, providing a more robust and holistic approach to creative thinking.
In the pursuit of innovation, it is essential to continually refine and enhance our thinking frameworks. The enhanced SCAMPER method empowers individuals and organizations to unlock their creative potential. By leveraging the seven thinking techniques – Substitute, Combine, Astrict, Modify, Platform, Eliminate, and Reverse – we can push the boundaries of innovation and uncover remarkable ideas. Embrace this improved methodology to transform your problem-solving approach and unleash a new wave of innovation within your organization.

